What is Customer Churn: Causes, Types, and Prevention

Customer churn, driven by cancellations and payment failures, is an inevitable issue for every SaaS business. It silently chips away at your bottom line and, over time, can significantly harm your company's health.
Read further to find out how to grow revenue and break through a looming growth wall by reducing customer churn.
Key Highlights:
- Churn isn’t just a number; it shows how well your product or service keeps delivering value over time.
- Different churn types (voluntary, involuntary, avoidable, by lifecycle stage) need different solutions.
- Reducing churn boosts LTV, lowers pressure on acquisition, and maintains sustainable SaaS growth.
What is Customer Churn?
Customer churn, also known as user churn or customer attrition, is the number of customers who canceled their subscriptions during a given period.
Churn is the loss of existing customers that puts the brakes on growth and forces you to constantly replace them just to stay the same size.
A high churn rate signals a mismatch between your product, pricing, customer experience, or market fit. It’s important to calculate, monitor, and measure churn because getting new customers is always more expensive than keeping existing ones.
Churn Benchmarks Across Different Business Models and Industries
Customer churn rates vary by industry, business model, and how often customers interact with the product. For example, in SaaS, churn is typically measured as a monthly percentage of customers or MRR lost. Average annual churn for B2B SaaS is around 3–5%, while B2C-focused SaaS businesses often see monthly churn closer to 6–8%. Early-stage SaaS companies typically face higher churn than larger, more established companies.
In e-commerce, churn is reflected in low repeat-purchase patterns rather than subscription cancellations. According to Shopify, around 75% of e-commerce customers never make a second purchase. Churn rates also differ by industry; for example, in regulated sectors like fintech, banking, and insurance, churn can be influenced by trust, switching costs, and complexity. If you’re looking for benchmarks, the table below shows average churn rates for several industries.
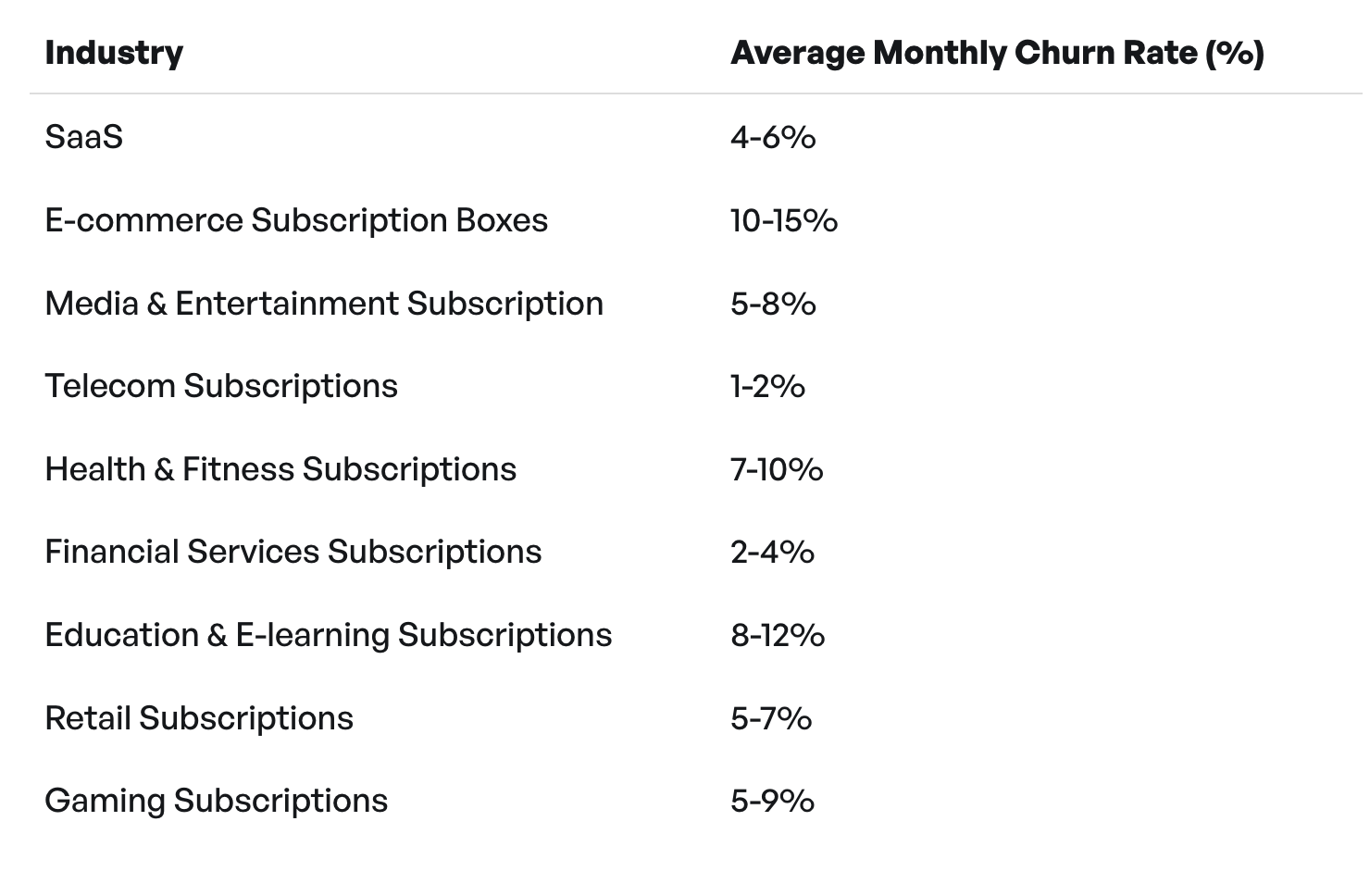
Each business model and industry has its own churn rates, so your strategy needs to follow your customers’ actual churn patterns, not a generic benchmark.
How to Calculate the Churn Rate for A SaaS Company?
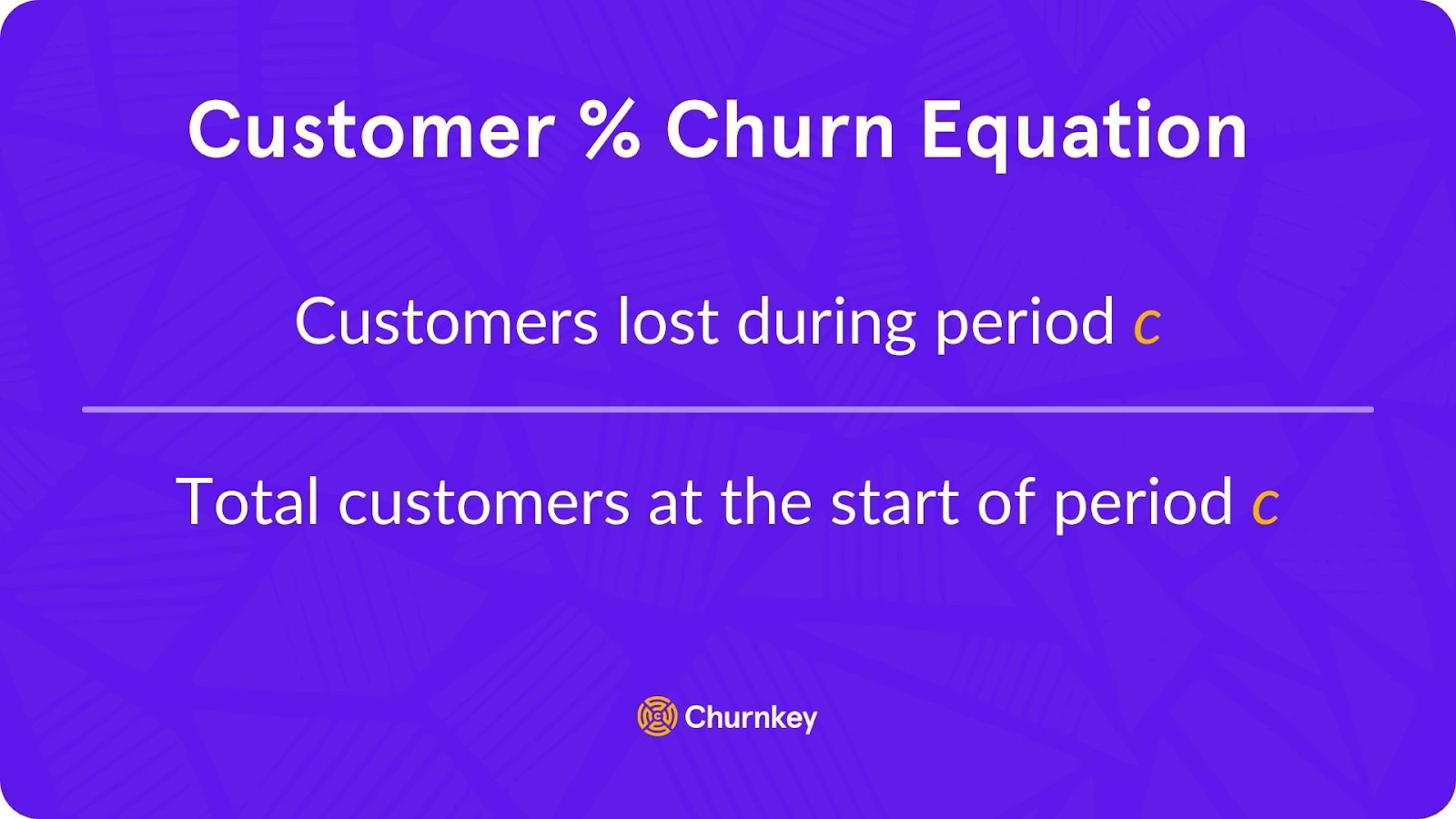
The basic formula for customer churn rate is: Churn rate = (Number of customers lost during the period ÷ Number of customers at the start of the period) × 100. You should exclude new customers acquired during the period from the calculations, because they were not “at risk” for the time period. For example, if you start the month with 1,000 customers and 100 of them churn by the end, your monthly churn rate is (100 ÷ 1,000) × 100 = 10%.
However, it’s easier to use an online churn rate calculator to quickly apply the formula across different periods and scenarios. If you are a SaaS business, check our step-by-step churn calculation guide.
A Case Study
To see the effect churn has on your medium- to long-term growth, consider a hypothetical business. Let's call the company SienarCast, which:
- has 10,000 customers
- adds 2,000 customers per month
- makes an average of $19 per user
- has a monthly churn rate of 10%
With that churn rate, SienarCast will hit a growth wall around six months.
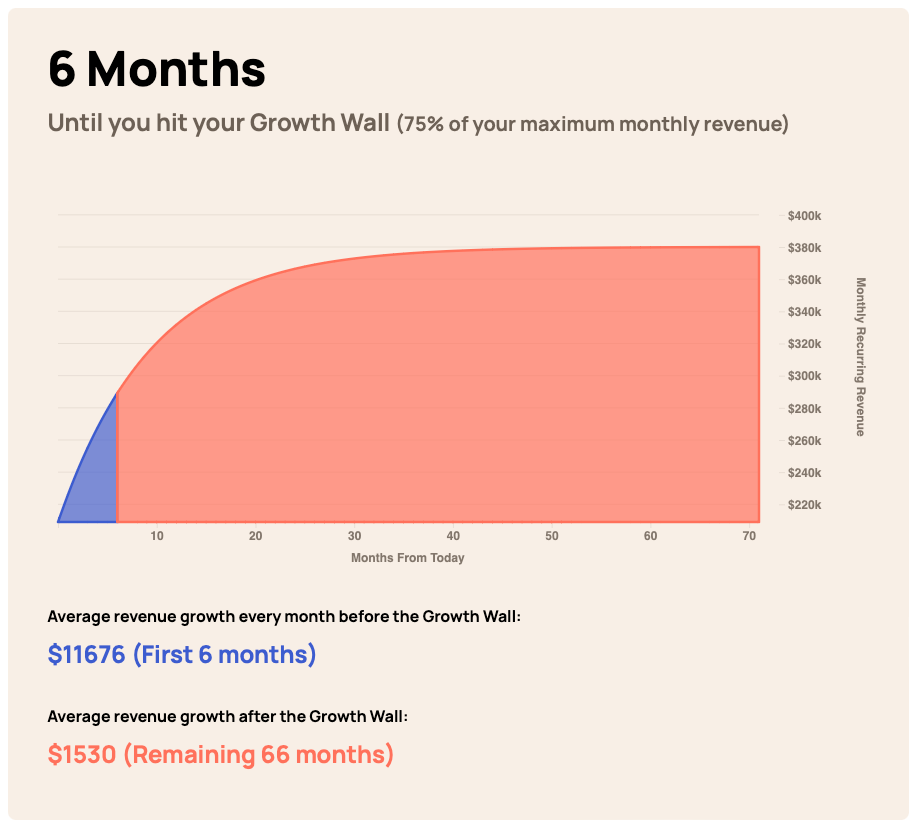
Now, let's cut that churn rate in half to 5%.

Suddenly, SinearCast's MRR growth extends to 21 months.
Customer Churn Types
Understanding customer churn types helps you understand why and when customers leave. This allows you to respond with the right fixes and offers.
- Voluntary churn happens when a customer decides to cancel, downgrade, or not renew their subscription. Some of the common reasons are perceived lack of value, product misfit, better alternatives, poor onboarding, or incorrect pricing model.
- Involuntary churn occurs when a customer loses a subscription without intending to, most commonly because of failed or expired payment methods.
- Avoidable churn refers to customers who unsubscribe for reasons you could have easily influenced, such as poor onboarding, confusing UX, slow support, or unclear pricing.
- Unavoidable churn happens when the customer’s need for the product or the service disappears. For example, a business closes or changes its model.
- Early churn occurs in the first part of the customer lifecycle, most likely within the trial period or the first 3 billing cycles.
- Mid-lifecycle churn happens after customers have been actively using the product or service for some time, but have not yet become truly invested.
How does Customer Churn Impact SaaS Businesses?
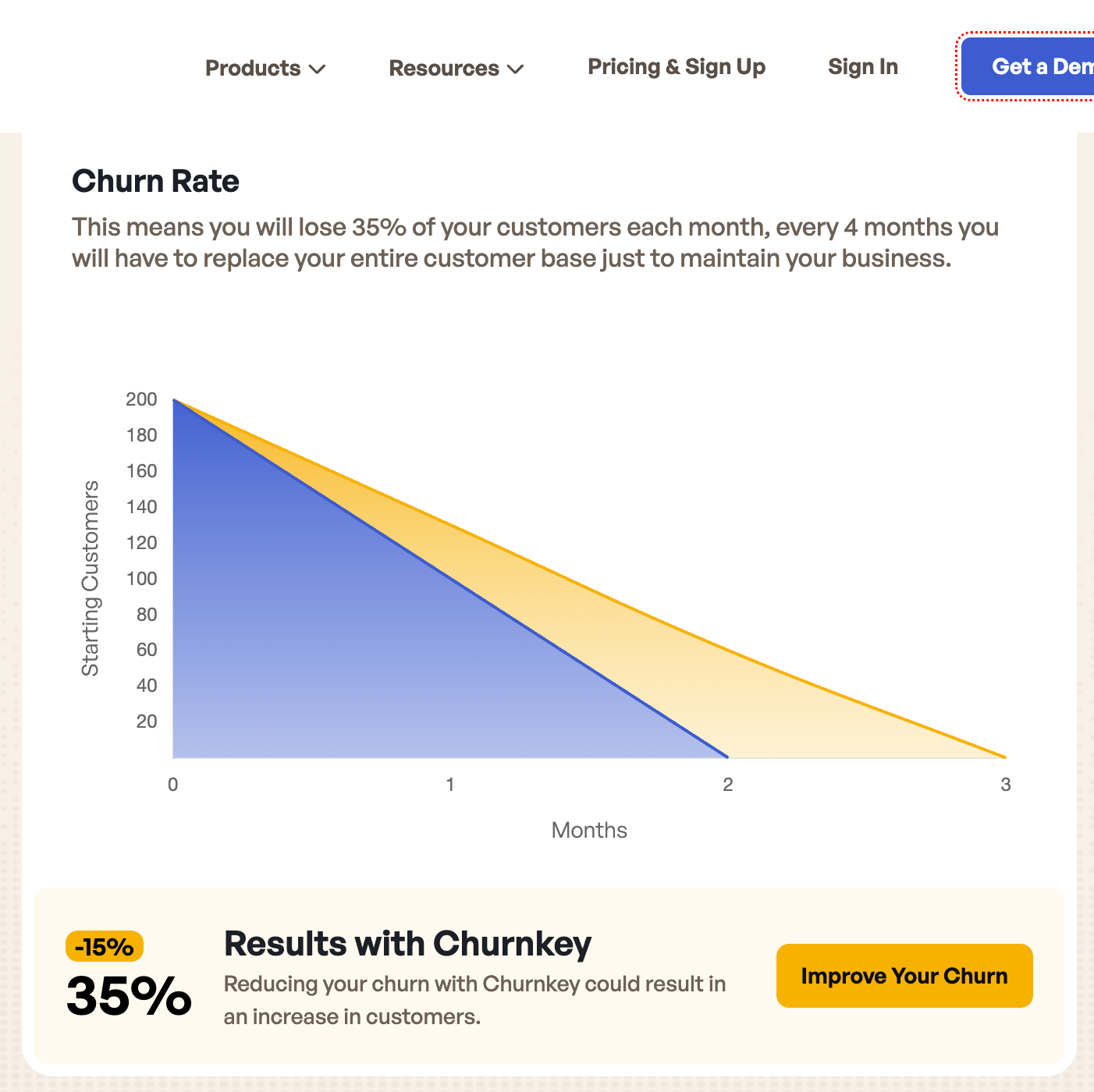
Of all the metrics associated with SaaS businesses, customer churn is arguably the most important because, in a subscription-based business model, your company’s overall revenue is tied directly to sustaining that recurring customer relationship.
- Customer churn affects recurring revenue. And monthly recurring revenue, or MRR, is what sustains any SaaS business.
- Churn increases your costs and drives up CAC, as you’re forced to invest more money into new customer acquisition just to stay flat.
- High churn destroys LTV (check the lifetime value calculator), limiting how much you can spend to win customers in the first place.
- Customer churn makes it harder to improve customer engagement because existing customers are more likely to spend more money than new customers.
Growth isn’t just new signups; it’s new customers minus churn. Churn is the part of the equation that quietly cancels out your acquisition wins.
What are the Common Reasons and Causes of Customer Churn?
Before creating an action plan to decrease churn rate, you have to dig into the root of your customer churn issue.
How to Reduce Customer Churn Over Time?
Churn isn’t reduced by one-off “win back campaigns.” It’s about building a steady system that lowers churn quarter after quarter. Long-term churn reduction has three pillars:
- Collecting data to understand why customers leave.
- Planning and fixing structural issues in your product.
- Automating processes to quietly do the heavy lifting in the background.
A good starting point is to separate churn types and handle them differently: voluntary vs involuntary, early vs late, low-fit vs high-fit customers. Here are more common reasons for churn:
- Identify the reasons for churn
- Set short-term and long-term churn reduction goals
- Collect data, ask for feedback from your customers, and analyze the patterns
- Target the right audience
- Offer long-term contract
- Prioritize high-value customers
- Engage with your customers and address their issues promptly
- Deliver exceptional customer service
- Offer loyalty programs
- Prioritize customer onboarding
- Reduce involuntary churn through smart payment recovery
How to Manage Customer Churn?
Managing customer churn is only possible with effective systems and processes in place. Once you’ve taken the time to determine what factors are driving churn in your particular business, you can start using the appropriate strategies to address those specific issues.
Create Effective Cancellation Flows
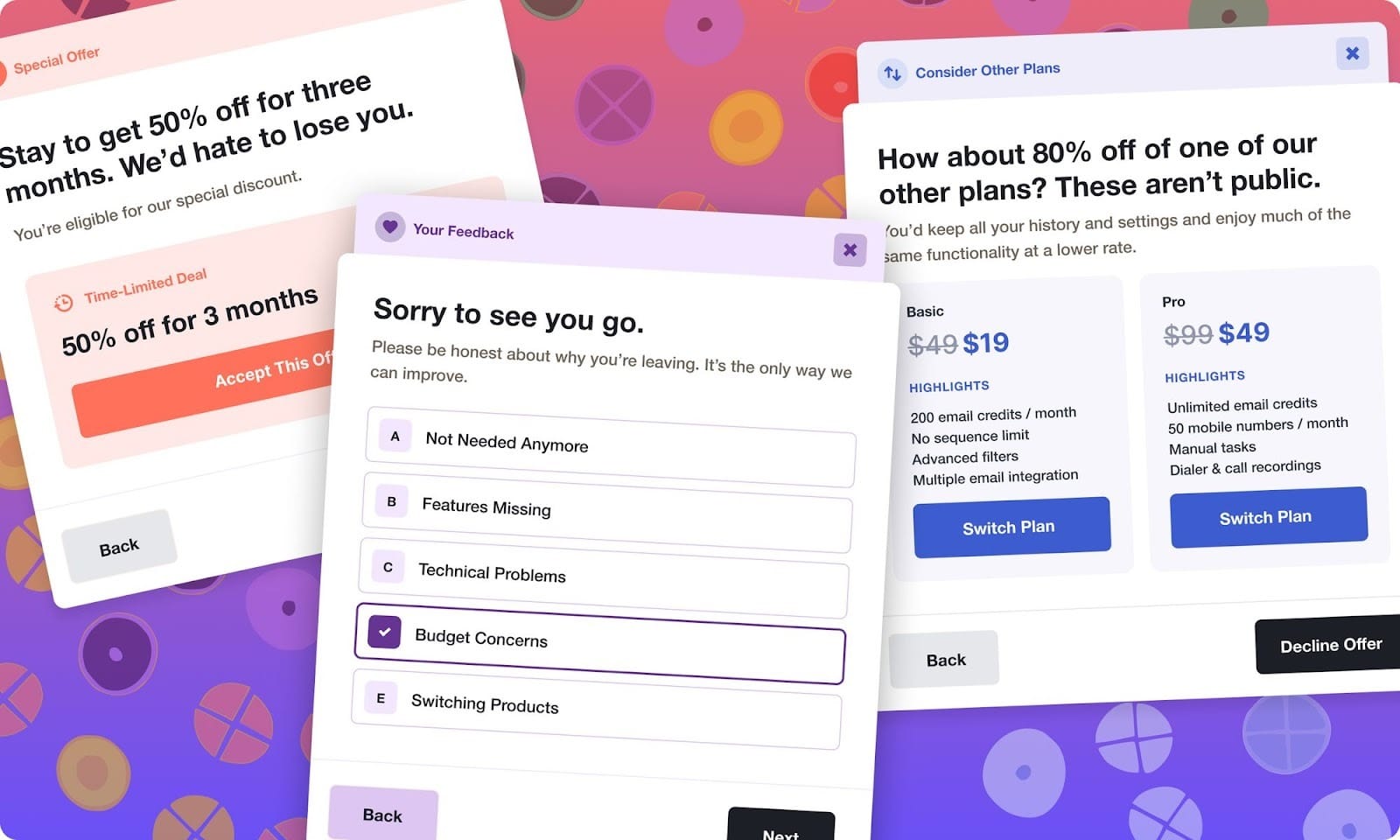
If the only thing standing between your customers and cancellation is a big “Cancel my subscription” button, then you’re missing out on a prime opportunity to prevent customer churn before it ever happens.
Start by asking the right customer exit survey questions. Always present a short-form, simple survey so that your customers are more willing to engage. The results will highlight where your product has the most opportunity to improve.
In our experience, an effective cancellation flow can not only help you reduce customer churn but also increase customer loyalty and provide valuable data on what drives customer cancellations.
☀️ With Churnkey, you can effortlessly set up a cancel flow to automatically reduce cancellations, making customers happier and driving more revenue.
Reduce Probable Churn
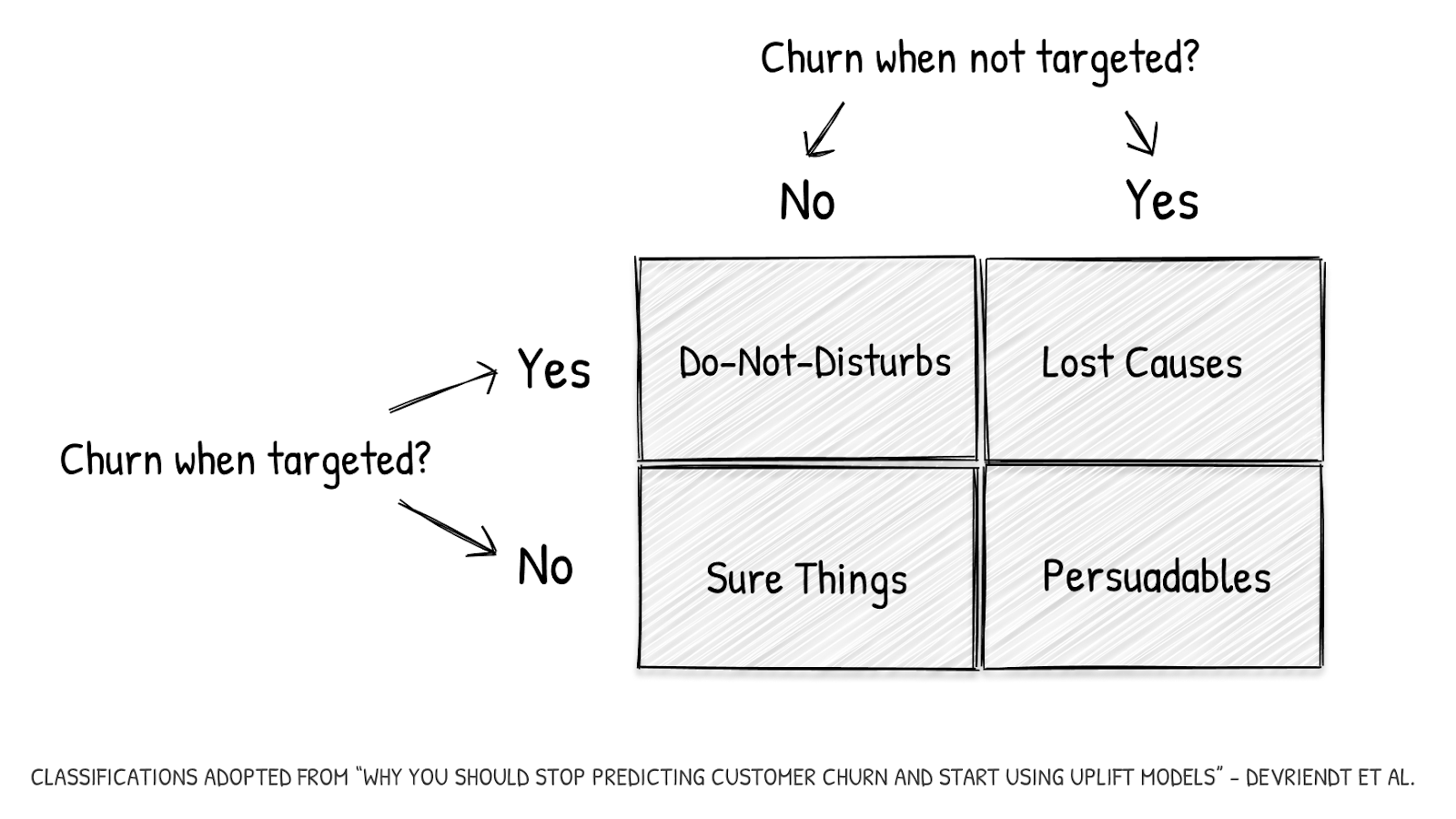
For most types of churn, you can easily identify at-risk customers, predict churn before it happens, and prevent it by addressing their concerns. One way to do that is to provide targeted, relevant offers or incentives to at-risk users to retain them as customers.
Handle Customer Churn Automatically
Modern SaaS companies rely on payment recoveries, payment retries, and AI feedback analysis to reduce churn. Automated cancellation flows can offer tailored options such as pauses, discounts, or downgrade paths, significantly reducing voluntary churn by providing customers a softer exit.
With Churnkey, you don’t have to worry about manually following up with each and every at-risk customer. Instead, you can identify and stop churn in its tracks before it occurs with customer-centric, user-friendly experiences. Are you ready to start combating customer churn? Schedule a demo and see how Churnkey is helping SaaS businesses reduce churn and retain more users.
Customer Churn Analysis and Measurement
Only identifying and fixing churn isn’t enough. You also need to implement ongoing customer churn analysis and measurement, combining quantitative data (e.g., product usage, billing events) with qualitative insights (e.g., exit surveys, interviews).
You must start by defining a set of core metrics, like logo churn, revenue churn, net revenue retention, and involuntary churn, and tracking them consistently over time. After that, segment churn by plan, ICP, acquisition channel, and other key attributes so you can clearly see the patterns and identify which cohorts are actually driving the problem.
Over time, systematic churn analysis creates feedback for product roadmap, pricing, onboarding, and customer success strategy.
Essential Tools for Measuring Customer Churn
For measuring and reducing churn effectively, you need more than a spreadsheet; you need a stack of tools that help you analyze, understand, and prevent customer churn. Here are the basic must-have tools:
Essential Churn Metrics to Track
To understand churn, you need to calculate different churn metrics that highlight different types of risk. When you use them together, they give you a clear, complete picture of your retention health.
- Customer churn rate is the percentage of customers who cancel their subscription or end their contract with a company over a specific period of time.
- Revenue churn rate is the percentage of recurring revenue lost over a specific period due to customer cancellations and plan downgrades.
- Gross churn rate is the percentage of revenue lost over a specific period due to customer cancellations and plan downgrades, without including new sales and expansions.
- Net churn rate is the percentage of revenue lost over a specific period due to customer cancellations and plan downgrades, after factoring in expansion and upgrades from existing customers.
Beyond direct churn metrics, you should also track other relevant financial metrics because customer churn directly affects a company’s financial performance. When customers churn, it reduces recurring revenue, slows down growth, and disrupts cash flow. The key financial metrics to track alongside churn are:
- Monthly Recurring Revenue (check our SaaS MRR Calculator)
- Annual Recurring Revenue (check our SaaS ARR Calculator)
- Customer Lifetime Value (check our SaaS LTV Calculator)
- CAC (read more about Customer Acquisition Cost)
- Expansion MRR
FAQ
What is the Difference Between B2B and B2C Churn?
B2B churn usually involves fewer customers with higher contract values and longer sales cycles. B2C churn tends to be higher-volume and more price- and habit-sensitive.
What’s the Difference Between Customer Churn and Customer Retention?
Customer churn measures the percentage of customers who leave in a given period, while customer retention measures the percentage who stay.
What is Gross Churn and Net Churn in SaaS?
Gross churn shows only the revenue lost from existing customers (cancellations and downgrades) over a period, ignoring any upgrades or expansion. Net churn offsets the lost revenue with expansion and upsell.
What is an Acceptable Churn Rate for SaaS?
“Acceptable” churn depends on your stage and market, but many B2B SaaS companies aim for 5% churn per month.



